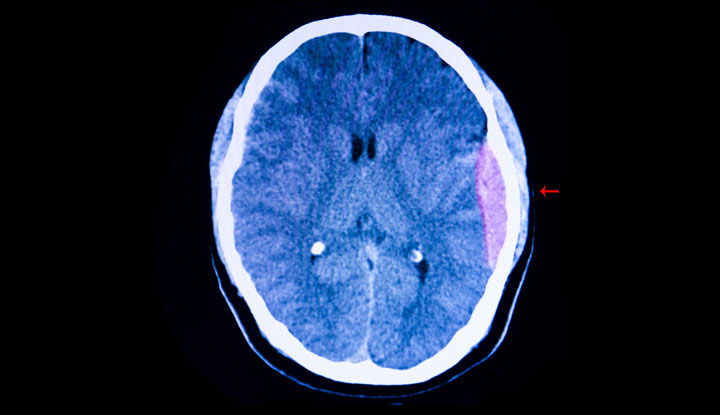


Epidural Hematoma
Epidural hematoma is a serious medical condition that occurs due to the accumulation of blood between the skull and dura mater (the outermost membrane of the brain), often developing after trauma.
Characteristics
It usually occurs following a blow to the head.
The most common cause is arterial bleeding, particularly the rupture of the middle meningeal artery.
The accumulation of blood grows rapidly, applying pressure on brain tissue.
Symptoms
A brief loss of consciousness may be followed by a "lucid interval" (temporary improvement), after which consciousness deteriorates again.
Severe headache
Nausea, vomiting
Changes in consciousness
Pupil dilation (anisocoria) and lateral deviation
Hemiplegia (loss of strength on one side of the body)
Diagnosis
CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Epidural hematomas typically appear as a biconvex (lens-shaped) hyperdense area under the skull.
Treatment
Emergency surgery: The hematoma is drained through a craniotomy, and the bleeding vessels are controlled.
Small, asymptomatic hematomas may sometimes be monitored.
Outcome
With quick diagnosis and treatment, full recovery is possible. Delayed intervention can be fatal.