Epilepsy surgery refers to surgical interventions performed in cases of epilepsy that cannot be controlled by medication (drug-resistant epilepsy). The goal of the surgery is to remove or control the source of the seizures.
Diseases
-

Epilepsy Surgery
-
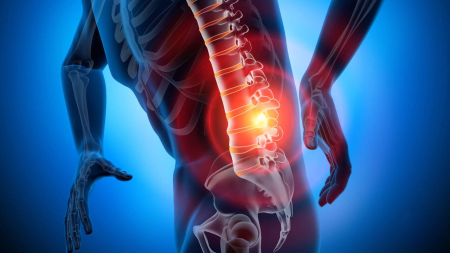
Lumbar Disc Herniation (Herniated Lumbar Disc)
Lumbar disc herniation is a condition that occurs when the discs located between the vertebrae shift out of place or when their outer layer tears, causing the gel-like inner material to protrude and put pressure on nearby nerves. This pressure can lead to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and muscle weakness.
-
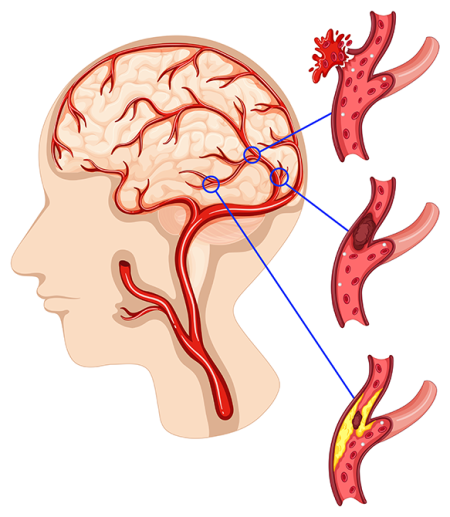
Brain Aneurysms
A brain aneurysm is a condition in which a weakened area in the wall of a brain artery expands and balloons out. An aneurysm often presents no symptoms and may go unnoticed, but if it ruptures, it can lead to a life-threatening brain hemorrhage known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
-
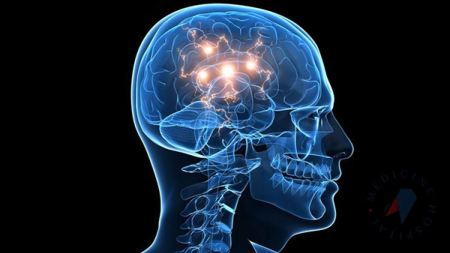
Arachnoid Cysts
Arachnoid cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or between the thin membranes called arachnoid mater, which cover the brain and spinal cord. These cysts typically contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and are most often congenital. In most cases, they do not cause symptoms, but large cysts may press on surrounding tissues and lead to clinical manifestations.
